

The UH ABC offers radial arm mazes for both mice and rats. Similar to the Morris Water Maze, special learning and memory in the radial arm maze is broadly hippocampal-dependent. Visits to an arm more than once or visits to non-baited arms count as working memory errors or reference memory errors, respectively. When used for assessing reference memory, only some of the arms contain a reward and the animal should only visit those baited arms. When investigating working memory, all arms are usually provided with a (food) reward and the animal should visit each arm only once. The radial arm maze is a paradigm that is used to assess spatial, working and reference memory in rats and mice. Data is generated by analyzing digital videos of the animal’s behavior using EthoVision XT 12.0. The UH ABC offers MWM for both mice and rats. In general, this behavioral assay is broadly hippocampal-dependent. Medications that increase central acetylcholine levels improve performance in the MWM whereas those that block cholinergic receptors decrease performance. Some genetically engineered mouse strains that model cognitive impairment in humans show impaired special learning. Animals undergo training sessions over days whereby they are given the opportunity to locate the platform using cues. The water maze consists of a pool, with a hidden platform submerged just below the surface of the water. The Morris Water Maze (MWM) is a popular behavioral assay for assessing spatial learning and memory. Digital videos of the animal’s behavior is analyzed using EthoVision XT 12.0 Body Recognition module. Other behaviors taken into consideration include distance traveled, velocity, freezing, and stretch-attend postures. Anxiolytics increase time spent in the center zone. Anxious animals spend more time around the perimeter (thigmotaxis) whereas animals that are not anxious spend more time in the center zone of the test arena. The amount of time spent close to the wall, time spent and number of entries into the center zone are key measurements.
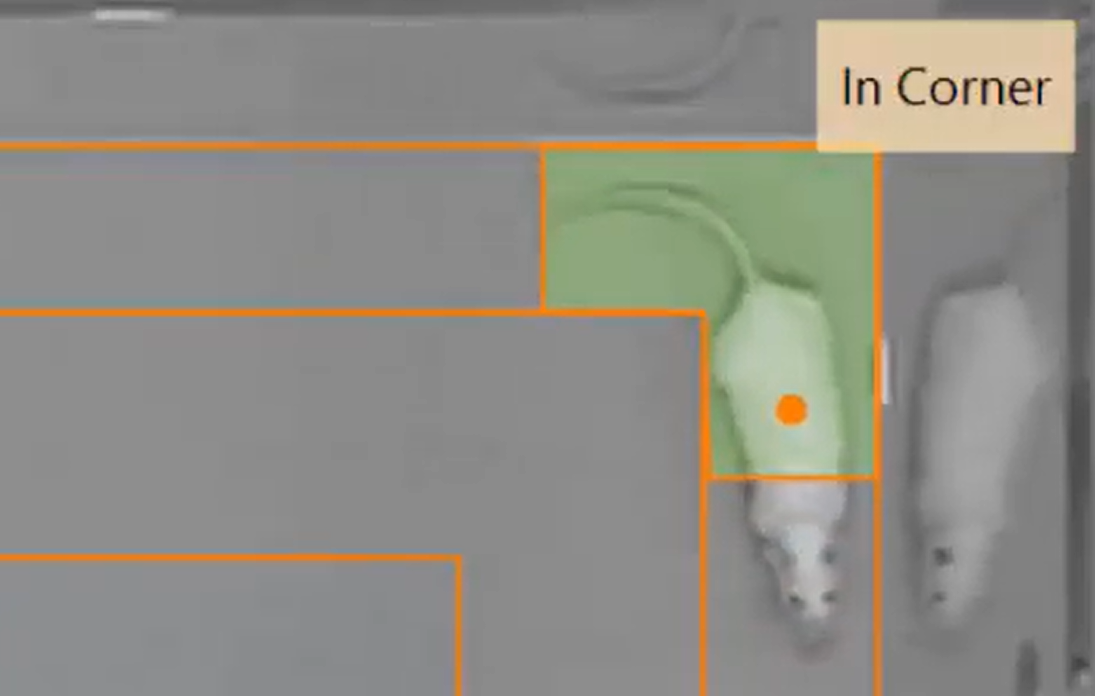

The open field consists of a square test arena, in which the animal’s activity is recorded with high-end digital cameras. The open field test is to assess locomotor activity, anxiety-related and exploratory behavior of rodents. Digital videos of the animal’s behavior is analyzed using EthoVision XT 12.0.
Any maze open field behavioral testing plus#
The UH ABC offers Elevated Plus Maze for both mice and rats. Anti-anxiety medications increase time spent on the open arms. In general, animals spend more time in the closed arms and less time on the open arms. The test relies upon the animal’s natural tendency to stay in enclosed spaces and fear of open spaces and heights. The maze consists of two open arms and two closed arms. The elevated plus maze is one of the most used behavioral tests for anxiety. Anxiety-like Behaviors Elevated Plus Maze


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
